Arterial Ulcers
LA Vascular Specialists
Vascular Specialists located in Beverly Hills, CA & Encino, CA
Arterial ulcers, also known as ischemic ulcers, are wounds that occur due to impaired blood flow to the affected area. These ulcers are often found on the lower extremities, such as the feet, ankles, and legs. They are characterized by a deep, irregular shape and a "punched-out" appearance with a pale or yellowish base. The edges of the ulcer are typically well-defined and may have a necrotic or black appearance.
Arterial Ulcers: Symptoms, Treatment Options, and More
Symptoms of arterial ulcers include severe pain, especially at night or when the affected limb is elevated. The pain is often described as a burning or throbbing sensation. Additionally, these ulcers may be slow to heal and tend to recur if not properly treated.
Treatment options for arterial ulcers focus on improving blood flow to the affected area. This may involve lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking and maintaining an active lifestyle. Medications can be prescribed to manage underlying conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to restore blood flow.
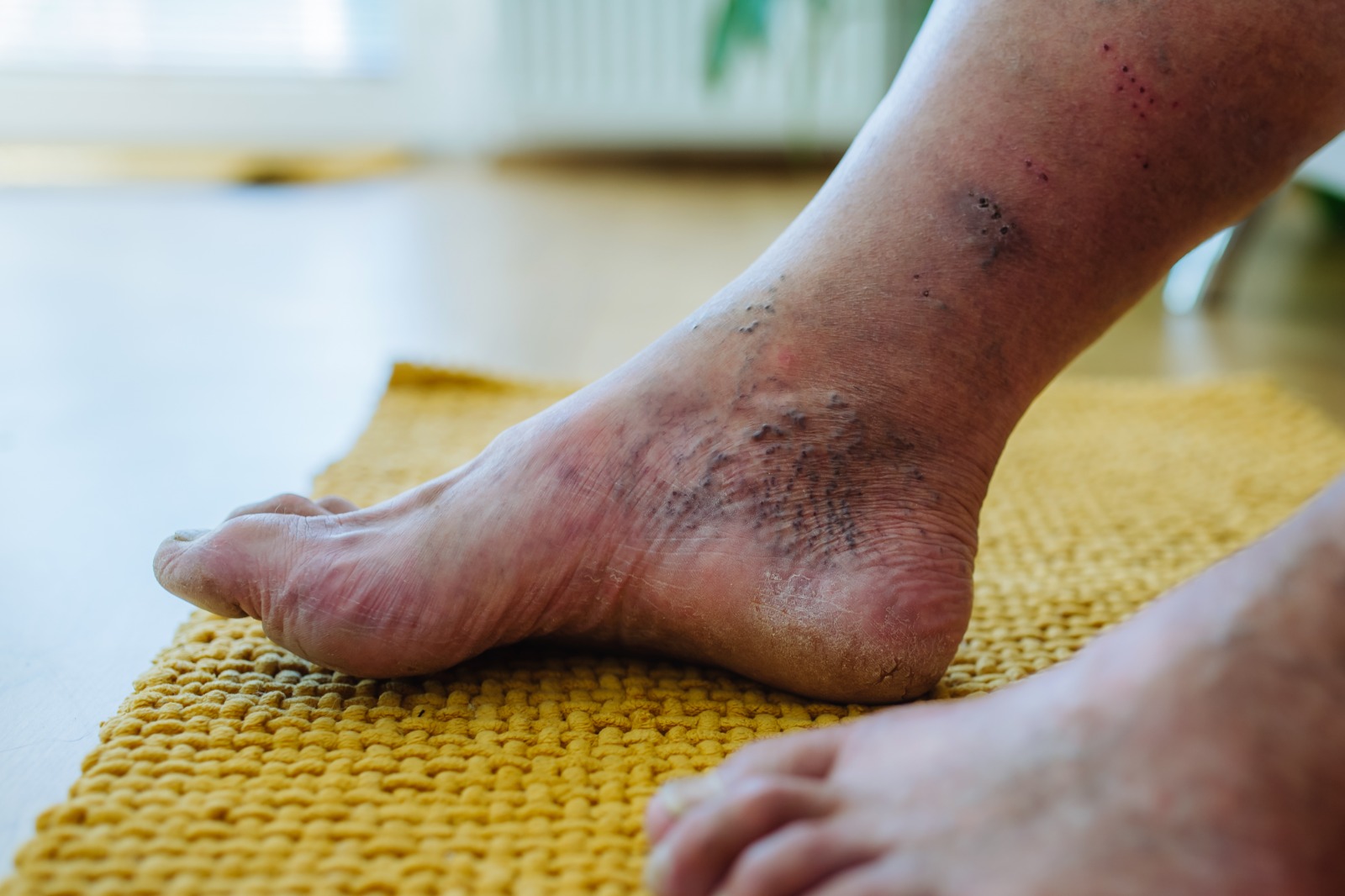
To assess for poor circulation, healthcare providers may check for weak or absent pulses, cool or pale skin, and delayed capillary refill. Ultrasounds or other imaging tests may also be conducted to evaluate blood flow to the affected area.
In conclusion, arterial ulcers are characterized by their appearance, severe pain, and association with poor circulation. Seeking prompt medical attention and following a comprehensive treatment plan is crucial to prevent complications and promote healing.
What are the symptoms of arterial ulcers?
Arterial ulcers are a common manifestation of peripheral arterial disease, a condition characterized by narrowed or blocked blood vessels in the lower extremities. Understanding the symptoms of arterial ulcers is essential in detecting and managing this condition.
Arterial ulcers typically exhibit distinctive characteristics. They often appear as deep, irregularly shaped wounds with well-defined edges. The color of these ulcers is usually pale or yellowish due to inadequate blood flow to the affected area. Additionally, the depth of arterial ulcers is often significant, as the underlying tissues are deprived of vital nutrients and oxygen.
In addition to their appearance, arterial ulcers present other signs that can aid in diagnosis. The affected limbs may feel cool to the touch due to reduced blood circulation. Likewise, minimal hair growth is observed, as the impaired blood supply starves the hair follicles of nutrients. The skin surrounding the ulcer is often tight and shiny, indicating tissue ischemia.
Individuals with arterial ulcers may experience various sensations related to the condition. Pain is a common symptom, typically described as a constant, throbbing discomfort. The legs may become reddened, reflecting the body's attempt to increase blood supply to the area. Moreover, delayed capillary return upon pressing the ulcer site is another characteristic of arterial ulcers.
In summary, arterial ulcers present distinct symptoms that include an irregularly shaped, pale or yellowish wound with significant depth. Coolness to the touch, minimal hair growth, and tight skin are additional signs. Patients may experience pain, leg reddening, and delayed capillary return. Prompt identification and management of arterial ulcers are crucial in preventing complications and promoting healing.
What is the primary cause of arterial ulcers?
The primary cause of arterial ulcers is arterial insufficiency, which refers to the reduced blood flow to the tissues in the extremities, particularly the legs and feet. Arterial insufficiency is commonly associated with a condition known as atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque within the arteries. This plaque is mainly composed of cholesterol, fatty deposits, and other substances.
Atherosclerosis causes the arteries to narrow and harden, resulting in decreased blood flow to the affected areas. The reduced blood flow deprives the tissues of oxygen and nutrients necessary for their proper functioning. Without an adequate blood supply, the tissues become progressively damaged, leading to the development of arterial ulcers.
Various factors contribute to the development of arterial ulcers in individuals with arterial insufficiency. These factors include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, diabetes, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and advanced age. Smoking is especially detrimental as it not only promotes the formation of arterial plaques but also constricts the blood vessels, further compromising blood flow.
The relationship between arterial insufficiency, atherosclerosis, and reduced blood flow is crucial in understanding the primary cause of arterial ulcers. Arterial insufficiency is a direct consequence of atherosclerosis, as the buildup of plaque within the arterial walls obstructs blood flow. The affected tissues become deprived of oxygen, leading to their gradual deterioration and the eventual formation of ulcers.
In summary, the primary cause of arterial ulcers is arterial insufficiency, which stems from the development of atherosclerosis and the resultant reduced blood flow to the tissues. Various factors contribute to the progression of arterial ulcers, emphasizing the importance of addressing underlying conditions and promoting healthy lifestyle choices to prevent their occurrence.
Caring for Arterial Ulcers at Home
Caring for arterial ulcers at home is crucial to promote healing and prevent infection. Here are the important steps to properly care for arterial ulcers:
1. Keep the ulcer clean: Gently wash the wound with mild soap and warm water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or scrubbing vigorously. Pat the area dry with a clean, soft towel.
2. Bandage the ulcer: Apply an appropriate dressing, recommended by your healthcare provider, to protect the ulcer from contamination and facilitate healing. Change the dressing regularly, as instructed, to maintain cleanliness and prevent infection.
3. Follow a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for wound healing. Include foods high in protein, such as lean meats, eggs, and legumes, to support tissue repair. Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
4. Take prescribed medications: Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics or wound healing medications to treat the arterial ulcer. It is crucial to take these medications as prescribed to prevent infection and promote healing.
5. Avoid compression therapy: Unlike venous ulcers, arterial ulcers are caused by inadequate blood supply. Therefore, avoid applying compression therapy, such as compression stockings or bandages, as it can further restrict blood flow and worsen the ulcer.
By following these steps, you can ensure proper care for arterial ulcers at home. Remember, maintaining cleanliness, eating a healthy diet, taking prescribed medications, and avoiding compression therapy are crucial for effective wound healing and preventing complications.
Medical Treatment of Arterial Ulcers
Arterial ulcers pose a significant challenge in wound care due to impaired blood flow to the affected area. The goal of medical treatment is to promote healing, protect against infection, and improve blood flow.
Non-surgical approaches are commonly used initially to treat arterial ulcers. The use of dressings plays a vital role in wound care management. Many different types of dressings are available, such as hydrogels, foam dressings, and alginate dressings, which absorb excess moisture and maintain a moist environment conducive to healing. Additionally, creams and ointments containing antimicrobial agents help prevent infection and promote healing.
To further aid in wound healing, medications such as topical vasodilators may be prescribed to increase blood flow to the affected area. These medications help dilate blood vessels, improving circulation and oxygen supply to the wound.
In cases where non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgical options may be considered. Surgical interventions aim to restore blood flow to the affected area, thus enhancing the healing process. Procedures such as bypass surgery can redirect blood flow around blocked arteries, while endarterectomy involves removing plaque from the artery walls. These procedures can improve blood flow and promote healing in arterial ulcers.
Minimally invasive interventional radiology procedures are an alternative to traditional surgery. These procedures involve the use of imaging guidance to thread catheters through blood vessels to reach the site of the blockage. Angioplasty can dilate narrowed or blocked arteries, while stenting involves placing a small mesh tube to keep the artery open. Atherectomy procedures remove plaque buildup from artery walls using specialized tools. These procedures help restore adequate blood flow to the affected area, facilitating ulcer healing.
In conclusion, the medical treatment of arterial ulcers encompasses a range of non-surgical and surgical options. Dressings, creams, ointments, and medications are used to stimulate healing and prevent infection. Minimally invasive interventional radiology procedures play a crucial role in improving blood flow and promoting ulcer healing. Through a combination of these approaches, patients with arterial ulcers can achieve successful wound management and optimal healing outcomes.
Conclusion: Arterial Ulcers
The conclusion for arterial ulcers is that prompt and effective treatment is crucial to prevent complications and promote healing. Arterial ulcers are a result of impaired blood flow to the lower extremities due to arterial disease, such as peripheral artery disease (PAD).
The key points to be addressed in the conclusion of arterial ulcers are the severity of the condition, the potential for complications, and the importance of timely treatment. Arterial ulcers are often chronic and non-healing, leading to significant pain, infection, and tissue loss. Without proper treatment, they can result in gangrene and ultimately lead to limb amputation.
The implications of arterial ulcers are vast, affecting the quality of life and overall well-being of individuals. They can cause severe pain, limit mobility, and increase the risk of infections. Timely treatment is vital to prevent further damage, promote healing, and reduce the risk of complications.
Treatment options for arterial ulcers include both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Lifestyle changes may include smoking cessation, maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Medical interventions may involve the use of medications to improve blood flow, such as antiplatelet drugs or vasodilators.
In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary. These can range from endovascular interventions, such as angioplasty or stenting, to bypass surgery to restore blood flow to the affected area.
In conclusion, arterial ulcers are a serious condition that require immediate attention and treatment. The implications of arterial ulcers can be debilitating, making timely intervention crucial. Treatment options encompass lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and surgical procedures to promote healing and prevent complications.
