Diabetic Foot Care Near Me
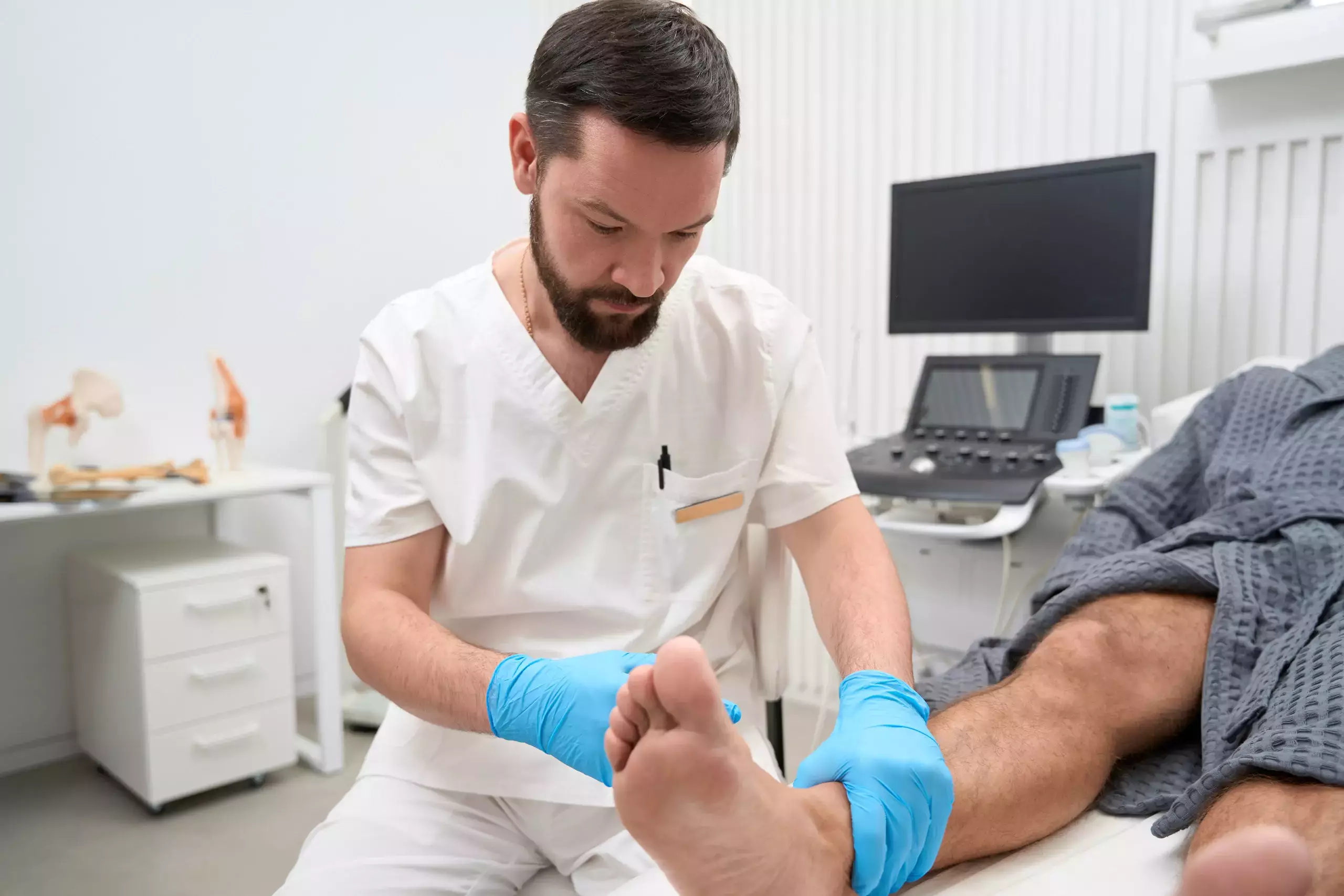
Introduction to Diabetic Foot Care Near Me
A Diabetic Foot Care Specialist is responsible for providing comprehensive care for diabetic patients, with a specific focus on the feet and ankles. They possess the knowledge and expertise to assess and manage the unique foot care needs of diabetic individuals, ensuring the prevention of complications and the maintenance of overall health.
To qualify as a Diabetic Foot Care Specialist, one must hold a relevant medical degree and complete specialized training in the field of diabetes and foot care. In addition, strong communication and interpersonal skills are essential, as they will work closely with patients, their families, and a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals.
One of the main responsibilities of a Diabetic Foot Care Specialist is to create individualized treatment plans for diabetic patients, taking into account their medical history, current foot health, and specific needs. They develop and implement strategies to minimize complications such as foot ulcers, infections, and amputations. This involves regular examination and assessment of circulation and nerve function in order to detect any abnormalities or signs of deterioration.
By conducting thorough assessments and monitoring, Diabetic Foot Care Specialists play a critical role in identifying potential risk factors and implementing preventive measures. They provide education to patients and their families, empowering them to engage in self-care practices and make informed decisions regarding foot health.
In summary, the primary responsibilities of a Diabetic Foot Care Specialist includes developing individualized treatment plans, minimizing complications, and regularly assessing circulation and nerve function in order to provide comprehensive foot care to diabetic patients.
How does my diabetes affect my feet?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, resulting in various complications throughout the body. One such area that can be significantly affected by diabetes is the feet. Due to high blood sugar levels and poor circulation, individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of experiencing foot problems. These complications can range from mild issues, such as dryness and calluses, to more severe conditions like neuropathy and foot ulcers. Understanding how diabetes impacts the feet is crucial for individuals with the condition to prioritize foot care and take necessary precautions to prevent complications that could significantly impact mobility and overall health.
Neuropathy Problem
Neuropathy refers to a condition that affects the nerves, resulting in various symptoms and complications. Individuals with neuropathy often experience burning sensations, tingling feet, cramping toes, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can significantly impact their daily lives and overall well-being.
The burning sensations experienced by individuals with neuropathy can range from mild discomfort to intense pain. This can make it difficult to engage in regular activities and negatively affect quality of life. Alongside burning sensations, a tingling sensation in the feet is commonly reported among those with neuropathy. This can lead to difficulty walking, as the tingling sensation may impair balance and coordination.
Furthermore, cramping toes are a frequent symptom of neuropathy. These muscle cramps can be painful and cause discomfort, making it challenging to wear shoes or walk comfortably.
Sleep disturbances are also a common complication of neuropathy. The persistent burning sensations, tingling, and cramping can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and decreased overall well-being.
Adequate sensation is crucial in preventing diabetic foot ulcers. Neuropathy can cause a loss of sensation in the feet, making it challenging for individuals to detect injuries such as cuts, blisters, or sores. Without proper sensation, these minor injuries can easily become infected and develop into diabetic foot ulcers. These ulcers are slow to heal and can lead to serious complications such as infections, gangrene, and even amputation.
In conclusion, neuropathy presents with symptoms such as burning sensations, tingling feet, cramping toes, and sleep disturbances. It is vital to maintain adequate sensation in order to prevent diabetic foot ulcers, as a loss of sensation can lead to serious complications. Individuals with neuropathy should seek medical attention and implement appropriate measures to manage their symptoms and prevent further complications.
Deformity Problem
The deformity problem refers to a physical abnormality or disfigurement that affects a person's appearance or motor function. In order to provide a detailed assessment of the deformity found, it is crucial to evaluate the extent and nature of the deformity.
Assessing a deformity involves observing and measuring the affected body part or area, noting any asymmetry, misalignment, or abnormal curvature. This can be done through visual inspection, palpation, range of motion testing, and potentially imaging techniques such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Additionally, assessing the patient's level of pain and functional limitations caused by the deformity is essential in order to fully understand the impact it has on their daily life.
Specific issues related to the deformity may vary depending on the type and location of the deformity. For example, in the case of scoliosis, a specific issue could be the significant spinal curvature, which can lead to breathing difficulties and compromised organ function. The presence of a limb length discrepancy might cause issues with walking and balance. Additionally, deformities can negatively affect body image and self-esteem, leading to psychosocial challenges for the individual.
Causes of deformities can be either congenital (present from birth) or acquired (developed later in life). Genetic factors, injury, disease, or external factors such as poor posture or repetitive stress can contribute to the development of deformities. Combining information from the patient's medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests can help determine the root cause or contributing factors of the deformity.
In conclusion, the deformity problem requires a thorough assessment to determine the extent, nature, and impact of the deformity on the individual's life. Understanding specific issues, causes, and contributing factors is essential in order to devise an appropriate treatment plan and improve the patient's quality of life.
Achilles Tendon Problems
Achilles tendon problems can be caused by a variety of factors. One common cause is overuse, which occurs when the tendon is subjected to repetitive stress and strain. This can be due to activities that involve jumping, running, or sudden changes in direction. Additionally, improper footwear can contribute to Achilles tendon problems by placing excessive pressure on the tendon or by not providing adequate support. Age-related degeneration is another factor that can lead to Achilles tendon issues, as the tendon becomes less flexible and more prone to injury over time.
The symptoms of Achilles tendon problems typically include pain, stiffness, and swelling in the back of the leg, near the heel. There may also be difficulty walking or bending the foot. If left untreated, these symptoms can worsen and lead to a partial or complete tear of the tendon.
Early diagnosis is crucial in the treatment of Achilles tendon problems. Rest and avoiding activities that aggravate the tendon are important first steps. Physical therapy can help to strengthen the tendon and surrounding muscles, as well as improve flexibility. In some cases, orthotic devices such as heel lifts or shoe inserts may be recommended. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the tendon.
Preventative measures play a key role in reducing the risk of Achilles tendon problems. Regular stretching exercises that target the calf muscles can help to maintain flexibility in the tendon. Strengthening exercises, such as heel raises, can also help to improve the overall strength of the tendon and surrounding muscles. It is important to listen to your body and rest when needed, as overuse can contribute to tendon issues. Choosing proper footwear that provides support and cushioning is also essential in preventing Achilles tendon problems. By taking these preventative measures and seeking early treatment, individuals can minimize the risk of developing Achilles tendon issues and improve their overall foot health.
Vascular Problem
Vascular problems can have a significant impact on blood flow to the foot and toe, leading to various complications. One common issue is restricted blood flow, which occurs when there is a narrowing or blockage in the blood vessels. This can be caused by a buildup of plaque or fatty deposits, known as atherosclerosis. Restricted blood flow can limit the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the foot and toe, leading to pain and discomfort.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is another vascular problem that affects blood flow to the extremities. In PAD, there is a narrowing of the arteries that supply blood to the legs and feet. This can result in decreased blood flow, causing pain, weakness, and cramping in the foot and toe muscles. In severe cases, PAD can lead to ulcers and even tissue death, known as gangrene.
Venous insufficiency is a condition that affects the veins in the leg, causing blood to pool and flow backward. This can result in swelling, pain, and ulcers in the foot and toe. Venous ulcers are typically located around the ankles and are slow to heal.
These vascular conditions can lead to various complications. Restricted blood flow, PAD, and venous insufficiency can cause pain due to inadequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the foot and toe tissues. The lack of blood flow can also impair the body's ability to fight infections, leading to the development of ulcers. Additionally, tissue death can occur in severe cases, which may necessitate amputation.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of these vascular problems. Smoking is a major risk factor as it damages and narrows the blood vessels. Individuals with a history of diabetes are also at an increased risk due to the damage high blood sugar levels can cause to the blood vessels. Poor circulation, often associated with conditions like obesity and sedentary lifestyle, can further increase the risk of vascular issues.
In conclusion, vascular problems such as restricted blood flow, peripheral artery disease, and venous insufficiency can significantly impact blood flow to the foot and toe. These conditions can lead to pain, ulcers, and other complications, often resulting from inadequate oxygen and nutrient supply to the tissues. Risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, and poor circulation contribute to the development of these vascular problems and should be managed to prevent their occurrence.
What symptoms will I feel in my feet from diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition characterized by the body's inability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. While diabetes can affect various parts of the body, one common area of manifestation is the feet. The feet are particularly susceptible to the adverse effects of diabetes as they are far from the heart, making it harder for blood to circulate properly. This can lead to a range of symptoms, some of which can be quite concerning. Understanding the symptoms that can affect the feet is essential for individuals with diabetes to seek timely medical attention and implement appropriate care strategies to prevent complications.
Tingling / Numbness
Tingling or numbness in the toes and feet can be caused by various factors, with one common underlying condition being neuropathy. Neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the nerves, often resulting from diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, alcohol abuse, trauma, or infections.
If left untreated, neuropathy can lead to severe consequences. One potential consequence is bone breakdown or osteoporosis. When the nerves are damaged, they fail to send proper signals to the bones, leading to decreased bone density and increased fragility. This can result in fractures and deformities in the feet, making walking and daily activities challenging.
Moreover, untreated neuropathy can progress to the point of necessitating amputation. In severe cases, the lack of sensation in the toes and feet can make it difficult to detect injuries or infections. Without timely treatment, these wounds can worsen, leading to gangrene, which may require amputation to prevent the infection from spreading further.
To address and manage neuropathy, early intervention is crucial. Firstly, determining and treating the underlying cause is essential. For example, controlling blood sugar levels in diabetes or addressing nutritional deficiencies. Additionally, medication such as pain relievers or nerve-modifying drugs may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle modifications can also help manage symptoms and slow down the progression of neuropathy. These include maintaining proper foot hygiene, wearing comfortable footwear that minimizes pressure on the feet, and performing regular exercises to improve circulation.
In conclusion, tingling or numbness in the toes and feet can be indicative of neuropathy. If left untreated, neuropathy can lead to severe consequences like bone breakdown and amputation. However, early intervention, identifying the underlying cause, and implementing lifestyle modifications can significantly improve the management of this condition.
Small Sores
Individuals with diabetes are susceptible to a variety of foot complications, one of which is the development of small sores. These sores can arise due to a combination of factors that are commonly associated with diabetes. Firstly, high blood sugar levels impair the body's ability to heal wounds efficiently. As a result, even minor injuries, such as small cuts or blisters, may take longer to recover in individuals with diabetes compared to those without the condition.
Moreover, neuropathy, a common complication of diabetes, can further exacerbate the issue. Neuropathy refers to nerve damage, which can lead to a loss of sensation in the feet. If a person cannot feel pain or discomfort in their feet due to neuropathy, they may overlook small sores, allowing them to go untreated.
Ignoring small sores in individuals with diabetes can have serious consequences. If left untreated, these small sores can progress into larger ulcers. Ulcers are open wounds that are prone to infection. They can become deep and severe, affecting the underlying tissues and bones. Delayed healing and the increased risk of infection can ultimately lead to the need for amputation in extreme cases.
To prevent such complications, it is crucial for individuals with diabetes to seek early treatment for small sores. This is where the expertise of a skilled and educated podiatrist comes into play. A podiatrist is a healthcare professional specializing in foot care. They possess the knowledge and experience to address diabetes-related foot issues effectively. Regular foot examinations by a podiatrist can help identify small sores and other potential problems before they escalate. By providing appropriate treatment and guidance on foot care, podiatrists play a vital role in preventing the development of larger ulcers and reducing the risk of amputation.
In conclusion, small sores in individuals with diabetes can pose significant risks if left untreated. The impaired healing and loss of sensation associated with diabetes can contribute to the progression of these sores into larger ulcers. Seeking timely assistance from a qualified podiatrist can help individuals maintain foot health, prevent complications, and secure a better quality of life.
How can I protect my feet if I have diabetes?
If you have diabetes, it is crucial to take extra care of your feet to prevent complications and maintain overall foot health. Here are the steps you can follow to protect your feet:
1. Daily Inspections: Perform a thorough examination of your feet every day. Look for any changes in color, skin integrity, or the presence of blisters, sores, or cuts. This will enable you to detect any issues early on.
2. Moisturizing: Keep your feet well-moisturized to prevent dryness and cracking. Use a gentle, unscented moisturizer and apply it daily, except between the toes.
3. Avoid Tight Socks and Shoes: Wear proper-fitting shoes and socks to prevent rubbing and pressure points. Avoid tight footwear that can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of foot problems.
4. Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels: Consistently manage your blood sugar levels within the target range recommended by your healthcare provider. High blood sugar can negatively impact foot health by reducing circulation and impairing healing.
5. Treatment and Prevention: If you notice any issues such as cuts, sores, or infections, seek immediate treatment from a healthcare professional. Additionally, to prevent chronic foot problems, consult with your doctor or a podiatrist for a comprehensive foot care plan.
In conclusion, protecting your feet if you have diabetes involves daily inspections, moisturizing to prevent cracking, wearing comfortable footwear, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, and seeking timely treatment and prevention. By following these steps, you can safeguard your feet and lower the risk of diabetes-related foot complications.
Diabetic Foot Care & Treatment
Diabetic Foot Care & Treatment is of utmost importance for individuals living with diabetes. Diabetes can lead to a number of complications, and one of the most common ones is peripheral neuropathy, which affects the nerves in the feet. This condition can cause loss of sensation in the feet, making it difficult to detect injuries, infections, or ulcers. Consequently, proper foot care and timely treatment are crucial to prevent serious complications such as foot ulcers, gangrene, and even amputation. Diabetic foot care involves a comprehensive approach that includes daily foot inspections, proper hygiene, regular visits to healthcare professionals, wearing appropriate footwear, maintaining blood glucose levels, and following a healthy lifestyle.
Additionally, treatment options for diabetic foot issues vary, ranging from wound care and infection management to surgical interventions if necessary. By following the recommended foot care practices and seeking prompt treatment, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of developing severe foot complications, ensuring long-term foot health and overall well-being.
Will insurance cover diabetic foot care near me?
Insurance coverage for diabetic foot care varies depending on the types of insurance plans and providers available in your area. Generally, most health insurance plans provide coverage for diabetic foot care to some extent. These may include private health insurance plans, employer-sponsored plans, Medicaid (for those who qualify), and Medicare (for individuals aged 65 and older or with certain disabilities).
Specific insurance providers that offer coverage for diabetic foot care may vary depending on your location. However, some commonly known providers include Blue Cross Blue Shield, Aetna, Cigna, UnitedHealthcare, and Humana. It is essential to check with your insurance company or healthcare provider to determine if they cover diabetic foot care, and to what extent.
Out-of-pocket costs related to insurance coverage for diabetic foot care may include copayments, deductibles, and coinsurance. These costs can vary depending on the insurance plan you have and the specific services received. It is important to review your insurance policy or contact your insurance provider to understand the potential out-of-pocket costs associated with diabetic foot care.
In conclusion, insurance coverage for diabetic foot care near you will depend on the types of insurance plans available, the specific insurance providers in your area, and the out-of-pocket costs associated with the coverage. It is crucial to research and consult with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage available to you.
The Importance of Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetic foot care is of utmost importance in the management of diabetes because it plays a crucial role in preventing complications that can arise from the disease. For individuals with diabetes, the risk of developing foot infections, foot ulcers, and poor circulation is significantly higher compared to those without diabetes.
Diabetes impairs the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, this can damage the blood vessels and nerves in the feet, resulting in poor circulation and neuropathy. Neuropathy, or nerve damage, makes it difficult for individuals with diabetes to feel heat, cold, or pain in their feet, making them more susceptible to injuries. Foot ulcers, which are open wounds, can develop due to the combination of decreased sensation and poor circulation. If left untreated, foot ulcers can become infected and may not heal properly.
Proper diabetic foot care is essential in preventing these complications. Regular inspection of the feet, including checking for cuts, sores, or blisters, is crucial. Maintaining good hygiene, such as washing the feet daily with warm water and mild soap, drying them thoroughly, and applying moisturizer to prevent dry skin, can all contribute to preventing complications. Wearing well-fitting, comfortable shoes and socks, and avoiding walking barefoot can also reduce the risk of injuries.
Failure to properly care for diabetic feet can have serious consequences. Non-healing wounds and infections can lead to more severe complications, such as gangrene and amputation. Additionally, neuropathy can cause balance issues and increase the risk of falls, further increasing the chances of foot injuries.
In conclusion, prioritizing diabetic foot care is essential in preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as infections, foot ulcers, and poor circulation. Proper foot care practices, including regular inspection and maintenance of foot hygiene, are crucial to avoiding serious consequences like non-healing wounds and neuropathy. By taking proactive steps to care for their feet, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce the risk of complications and maintain their overall health and well-being.
What Is Involved in Diabetic Foot Care?
Diabetic foot care is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and preventing complications. People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing foot problems due to poor blood circulation and nerve damage. Proper foot care involves several key elements, including daily hygiene routines, regular foot inspections, wearing appropriate footwear, managing blood sugar levels, and seeking immediate medical attention for any issues or injuries. By following these steps, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and amputations, ensuring their feet stay healthy and functional. It's important for individuals with diabetes to actively participate in their foot care and work closely with healthcare professionals to address any concerns or complications accordingly.
How can I get started with the best diabetic foot care near me?
If you are looking to find the best diabetic foot care near you, follow these simple steps to find your specialist.
1. Research and gather information: Begin by conducting thorough research online to find the most reputable and highly recommended diabetic foot specialists in your area. Look for specialists who have expertise in dealing with diabetes-related foot issues.
2. Check for professional credentials and experience: Once you have shortlisted a few potential specialists, take the time to review their professional credentials and experience. Look for certifications and qualifications that demonstrate their proficiency in dealing with diabetic foot conditions.
3. Read patient reviews and testimonials: Look for online reviews and testimonials from previous patients. This can provide insight into the quality of care provided by the diabetic foot specialists you are considering.
4. Schedule a consultation: Once you have identified a specialist that seems suitable, schedule a consultation either online or by calling the clinic directly. Many clinics offer the option to conveniently book appointments through their website.
5. Be prepared for the consultation: Before your consultation, gather all your medical records, including any previous diagnoses, test results, and medications. This will help the specialist understand your medical history and provide a more accurate assessment.
6. Attend the consultation: During the consultation, the diabetic foot specialist will assess your condition, discuss your symptoms, and conduct any necessary diagnostic tests or examinations. Be sure to communicate your concerns and ask any questions you may have.
By taking these steps, you will be on your way to finding the best diabetic foot specialist near you who can provide complete podiatric care for your specific needs.
